The new origami: Shape-changing ‘Kirigami’
A new shape-changing metamaterial using Kirigami, which is the ancient Japanese art of cutting and folding paper to obtain 3D shapes, has been developed by engineers from the University of Bristol. Metamaterials are a class of material engineered to produce properties that don’t occur naturally. Currently metamaterials are used to make artificial electromagnetic and vibration absorbers and high-performance sensors.
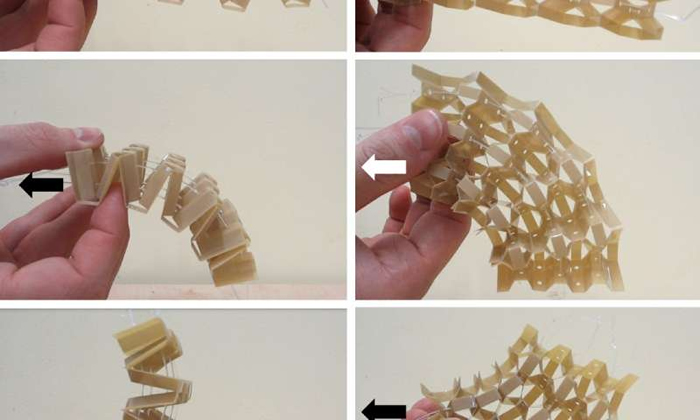
Kirigami can be applied to transform two-dimensional sheet materials into complex three-dimensional shapes with a broader choice of geometries than ‘classical’ origami.
The research, developed within a PhD program run by the University’s EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Advanced Composites for Innovation and Science (ACCIS CDT), is published in Scientific Reports.
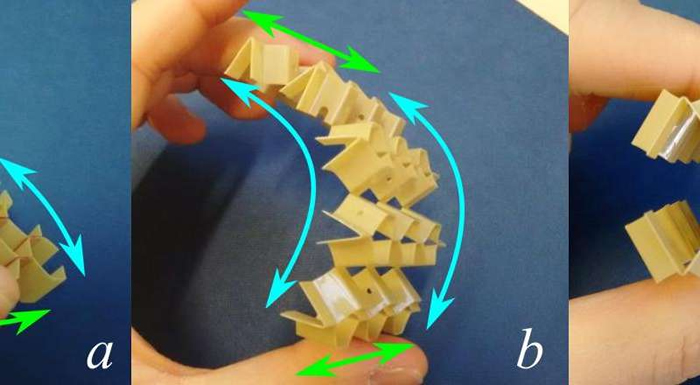
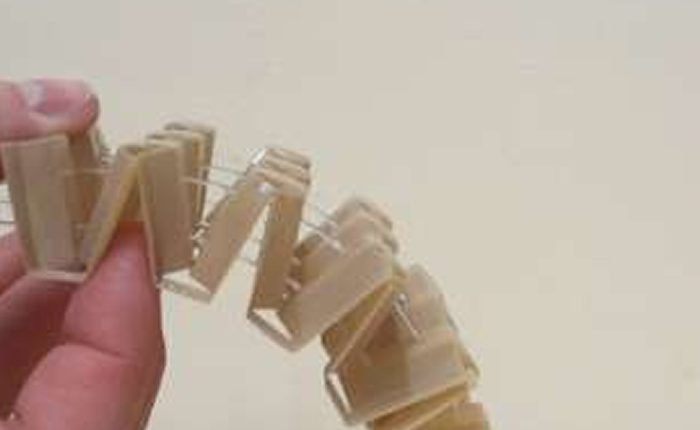
The type of mechanical metamaterials using the Kirigami technique, developed by PhD student Robin Neville, changes shape seamlessly, exhibits large variations in mechanical performance with small geometry changes, and can be adapted to modify its configuration by using mainstream actuation mechanisms.
The Kirigami metamaterial can also be produced using off-the-shelf thermoplastic or thermoset composite materials, and different sensing and electronics systems can be embedded to obtain a fully integrated smart shape-changing structure.
“Mechanical metamaterials exhibit unusual properties through the shape and deformation of their engineered subunits. Our research presents a new investigation of the kinematics of a family of cellular metamaterials based on Kirigami design principles, ” said Fabrizio Scarpa, Professor of Smart Materials and Structures in the Department of Aerospace Engineering and ACCIS.
“This technique allows us to create cellular structures with engineered cuts and folds that produce large shape and volume changes, and with extremely directional, tuneable mechanical properties,” Scarpa added.
“By combining analytical models and numerical simulations we have demonstrated how these Kirigami cellular metamaterials can change their deformation characteristics. We have also shown the potential of using these classes of mechanical metamaterials for shape change applications like morphing structures,” Robin Neville, PhD student, added.
In the future, this Kirigami metamaterial could be used in robotics, morphing structures for airframe and space applications, microwave and smart antennas.

More information: University of Bristol


Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.